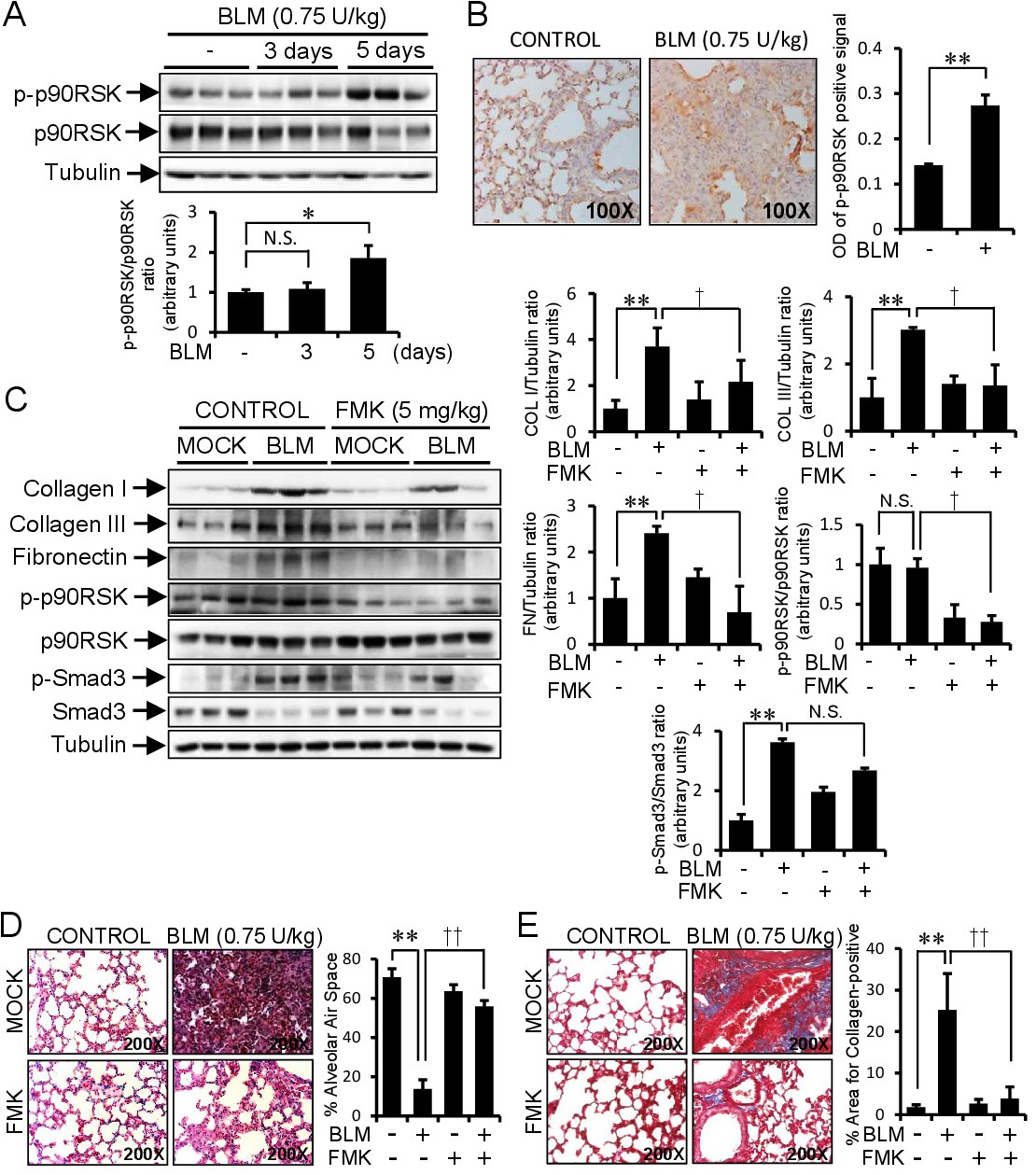
Fig. 7. FMK treatment ameliorated bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. A: Mice were examined at 3 or 5 days after the intratracheal administration of bleomycin (BLM) as described in the Materials and Methods (n=5). Lung tissue lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies for phospho-p90RSK, p90RSK, and tubulin. Bar graphs represent densitometric results of Western blot bands. B: To determine the in vivo effect of FMK (a specific p90RSK inhibitor) on pulmonary fibrosis induced by BLM, FMK was i.p. administrated to mice at 5 mg/kg every other day for 14 days. Mice were analyzed at 14 days after the intratracheal administration of BLM (n=5). Protein expressions of p-p90RSK in lung tissues were examined by immunohistochemistry. Positive signals of p-p90RSK in lung tissue sections stained with p-p90RSK antibody were measured with Fiji ImageJ2 software (NIH, MD, USA) and expressed as optical densities of positive signal (n=4). Data was presented as the Mean ± Standard Deviation. C: Mice were analyzed 14 days after BLM intratracheal administration in the presence or absence of FMK i.p. injection, as described in Material and Methods (n=5). Lung tissue lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies for collagen I, collagen III, fibronectin, p-p90RSK, p90RSK and tubulin. D: Histological sections of lung tissue were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The quantitative histological analysis of lung fibrosis was performed by measuring the alveolar air area in H & E stained lung tissues (n=4) using ImageJ version 1.52q (NIH, MD, USA) and expressed as the percentage of alveolar air area. Data was presented as the Mean ± Standard Deviation. E: Histological sections of lung tissue were stained with Masson Trichrome. The quantification of collagen-positive areas in Masson Trichrome stained lung tissues (n=4) were performed using ImageJ version 1.52q (NIH, MD, USA) and expressed as the percentage of collagen positive area. Data was presented as the Mean ± Standard Deviation. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01 versus CON. †, p<0.05, ††, p<0.01 versus TGF-β1 treated, N.S.: not significant.